Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a group of highly heterogeneous hematopoietic malignancies, often associated with acquired chromosomal abnormalities, the most common of which is chromosomal translocation. Chromosomal inversion of inv16 (p13q22) or translocation t(16;16) (p13; q22) found in myeloid leukemia (AML-M4) cells with eosinophilia, resulting in the MYH11 gene located at 16p13. The CBFB gene located at 16q22 is recombined to form a CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion. The detection rate of CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion in myeloid leukemia is about 7%. Since the CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion is only found in AML, according to the WHO leukemia diagnostic criteria, AML can be diagnosed by detecting the CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion.
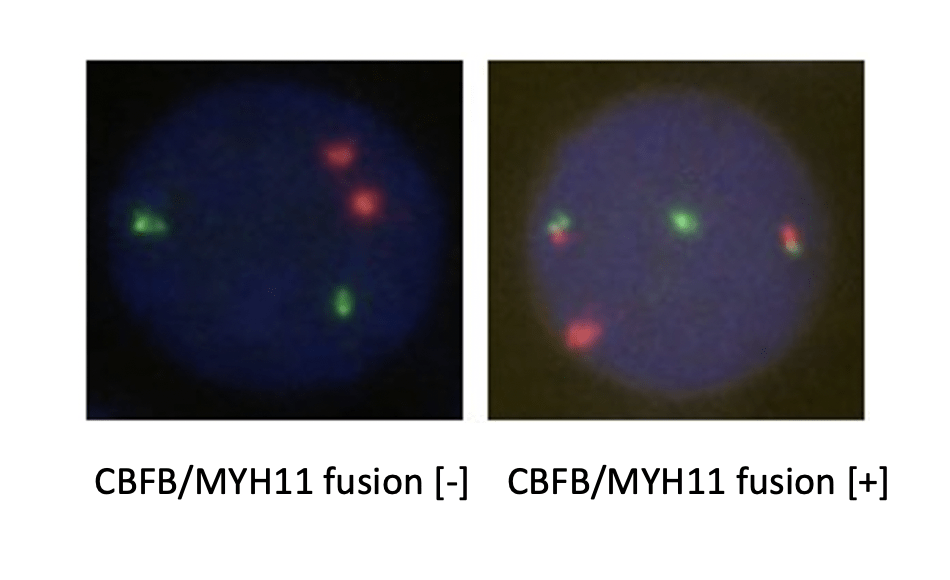
CBFB probe is labeled with an orange-red fluorescein, and MYH11 probe is labeled with a green fluorescein. The two probes combine to the target detection site by in situ hybridization. Under normal conditions (CBFB/MYH11 gene did not fuse), it shows two orange-red signals and two green signals under a fluorescence microscope. When a fusion gene is present, the green and orange-red signals form a yellow fusion signal due to recombination. The method was used to detect the status of CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion providing a reference for the identification, prognosis and drug administration guidance for clinical AML leukemia patients.

CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion can be used for the diagnosis of AML. In addition, in the case of positive CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion, the detection of CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion has become the most valuable indicator for the determination of therapeutic options and therapeutic efficacy evaluation. For example, quantitative analysis of CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion can also be used to judge the level of leukemia cells in patients, the detection of minimal residual disease and the prediction of recurrence risk. AML patients with CBFB/MYH11 gene fusion have a better prognosis, and high DFS and low recurrence rates can be achieved by HDAC regimen.
Product size: 100μL FISH probe ( ⬤ | ⬤ ) + Pretreatment reagent (10 tests) + Antifade staining solution DAPI (10 tests).